2019-数据结构-数据结构6.0-优先级队列
Priority Queues(优先级队列)
1. 优先级队列
- A priority queue is a collection of zero or more elements. Each element has a priority or value.一个优先级队列是0个或者更多元素的集合。每一个元素都有一个优先级或者值
- 进入队列的时候有优先级,出队列优先出高优先级的.
- 以下我们确定元素的优先级是通过数字的大小来确定。
1.1. 优先级队列分类(根据大小)
- In a min priority queue the find operation finds the element with minimum priority, while the delete operation delete this element.在最小优先级队列中,当需要删除一个元素的时候,我们找到优先级最小的元素来删除
- In a max priority queue, the find operation finds the element with maximum priority, while the delete operation delete this element.在最大优先级队列中,当需要删除一个元素的时候,我们找到优先级最大的元素来删除
2. 最大优先级队列(MaxPriorityQueue)
2.1. ADT(逻辑上最大优先级队列)
1 | |
2.2. 物理实现:Heap
- A max heap(min Heap):(最大堆)
- is A complete binary tree 最大堆是一个完全二叉树
- The value in each node is greater(less) than or equal to those in its children(if any).每一个节点上的值都大于(小于)或者等于他的子节点(如果有的话)
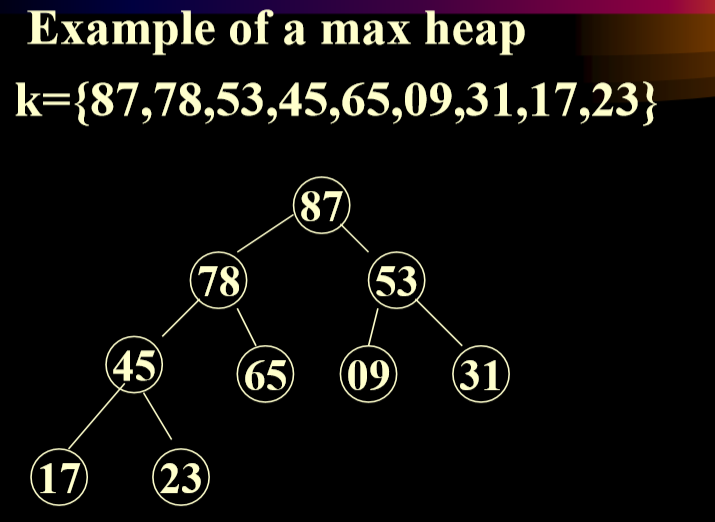
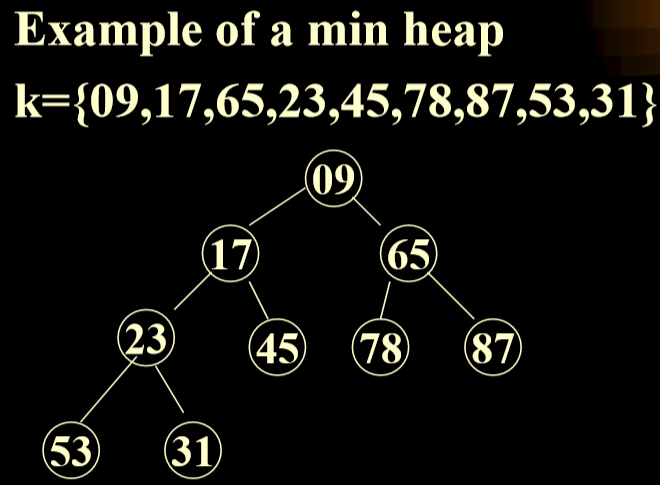
- 注意:完全二叉树可以用矩阵来进行存储。
- 从上向下一层一层进行记录。
2.3. 实现:最大优先级队列
1 | |
- 数组0号位置不用,也就是从Heap[1]开始使用
2.3.1. 最大堆的构造方法
1 | |
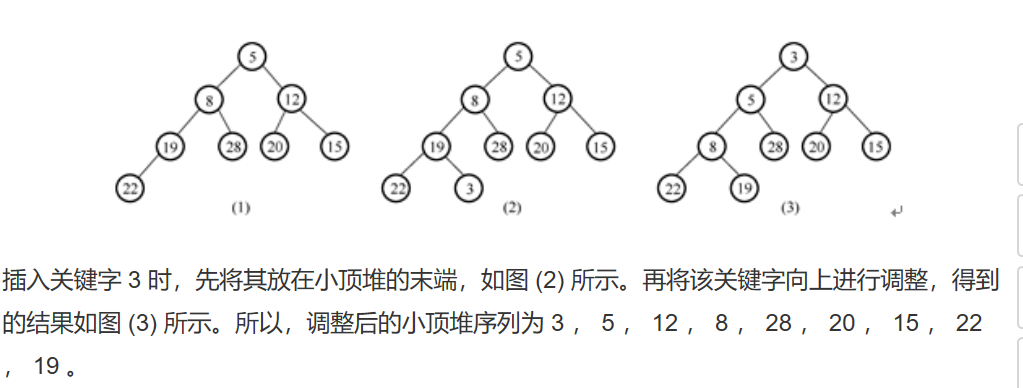
2.3.2. 最大堆的插入算法
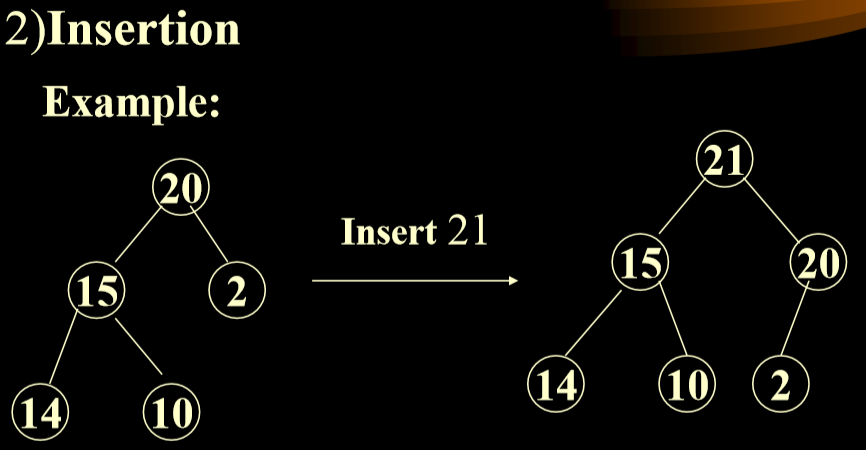
- 在数组后面插入后,和其父结点进行比较,如果比父结点大,则交换,一直到不再大于其父结点。
- 注意在最大优先级队列中的优先交换大的子树,不然会造成重复滤过。
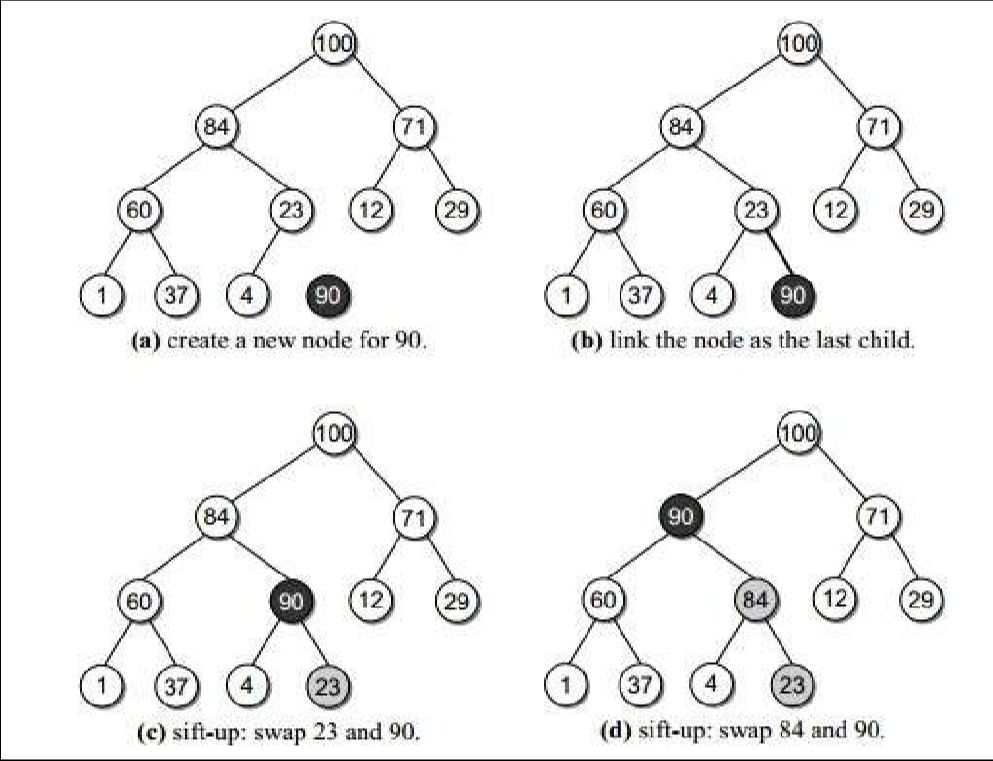
- 插入算法的时间复杂度:log2(n)
1 | |
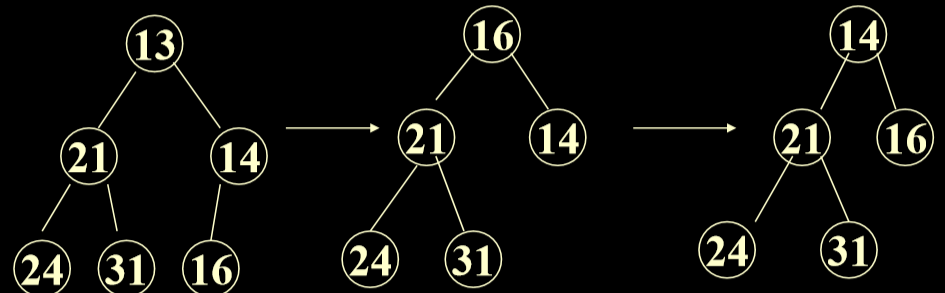
2.3.3. 最大堆的删除算法
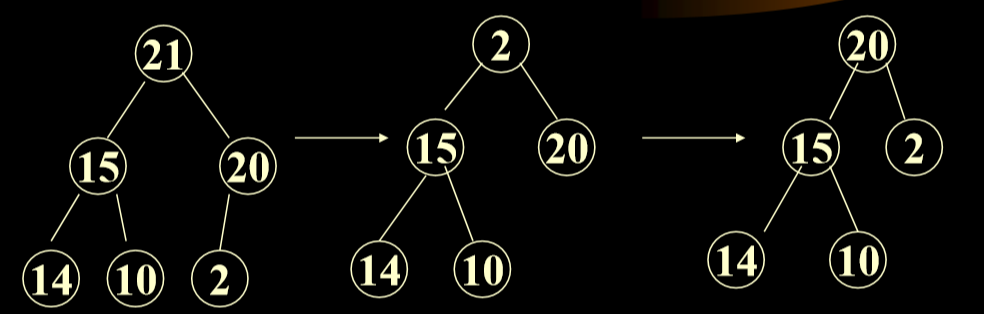
- 将根删除,将数组最后一个(最后一层最后一个元素)换为根,然后进行比较。
1 | |
- 插入算法的时间复杂度:log2(n)
2.4. 初始化一个非空的最大优先级数列
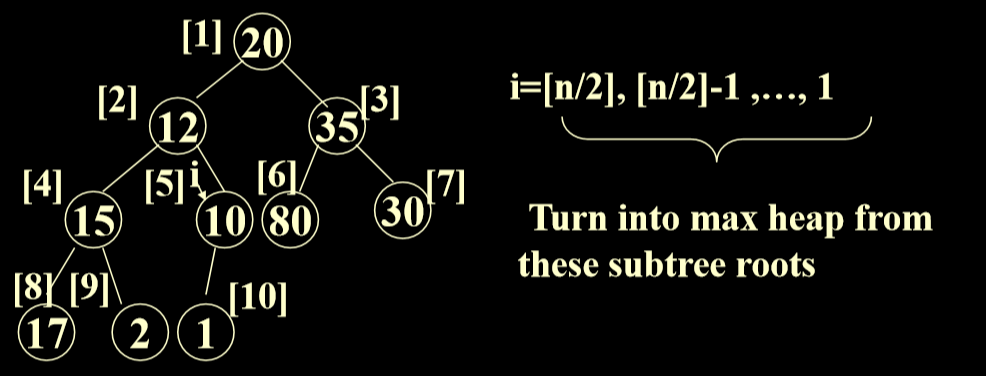
- 把初始指针指向最后一个节点的父结点(N/2)
- 然后进行循环,然后每一个都换一遍就完成。
- 总体来讲是从最后一个节点的父结点开始,对所有的非叶节点进行下滤操作。
- 对于某一层节点进行下滤后,对其父结点继续进行下滤。
1 | |
1 | |
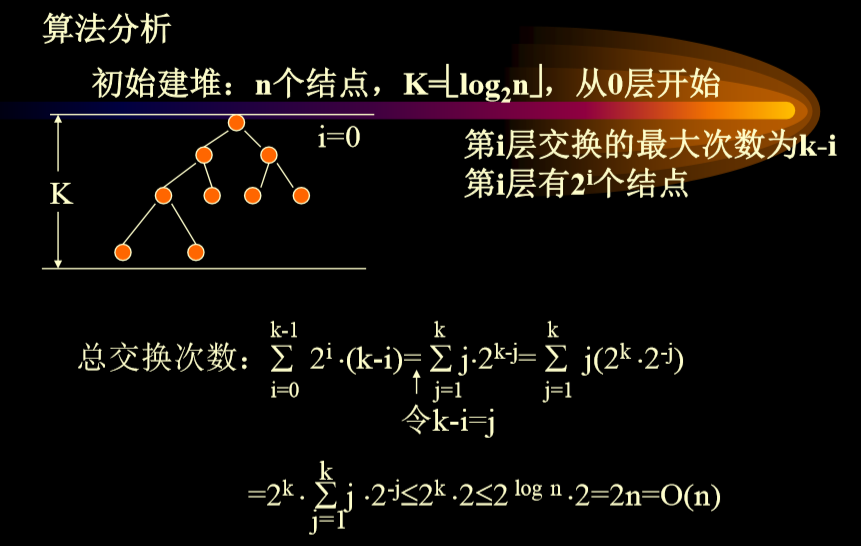
- 已经在内存中的算法复杂度分析(直接交换调整)
- 对于不同层的节点,其下滤的计算量时不同的
- 如何从感觉上立即这个问题:在数据的开始是不会到lgn的,而只有到后面的时候才能达到lgn(lgn = log2n)
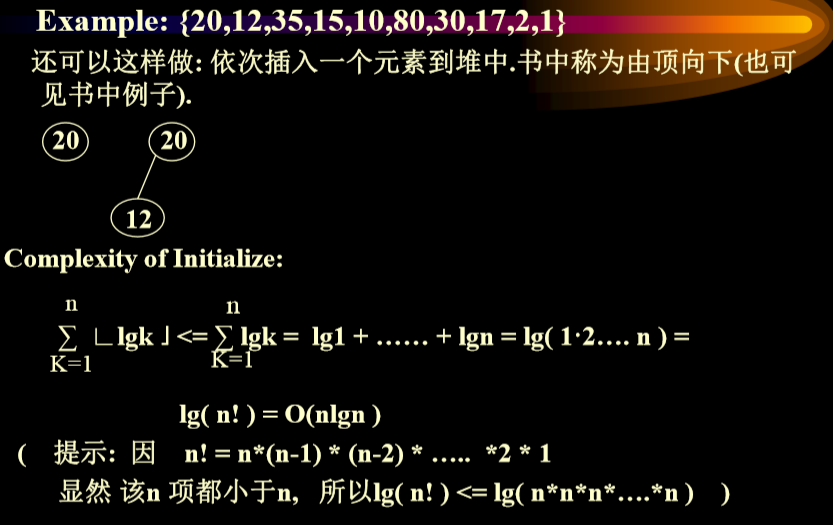
- 不在内存(插入)中的算法复杂度分析(需要上滤)(需要进行其他操作调整)
3. 实现最小优先级队列
1 | |
- 插入实例

1 | |
1 | |
- 删除实例
3.1. 参考
4. 优先级队列的应用
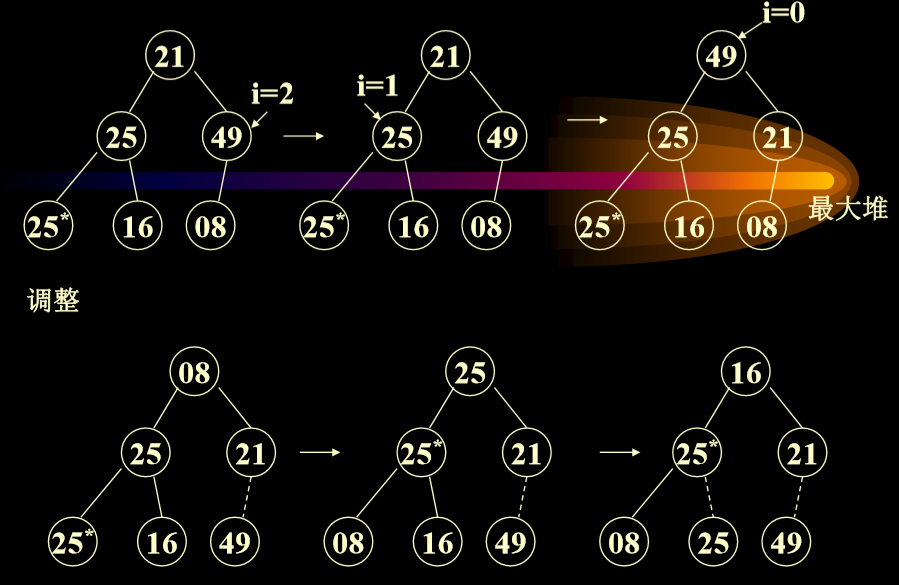
4.1. 堆排序(容易考)
- initialize a max heap with the n elements to be sorted O(n) 初始化一个n个元素的最大堆,O(n)
- each time we delete one element, then adjust the heap O(log2n) 每次我们删除最大的元素,调整堆的时间复杂度为O(log2n)
- Time complexity is O(n)+O(nlog2n)=O(nlog2n)
- 例子:{21,25,49,25*,16,08}
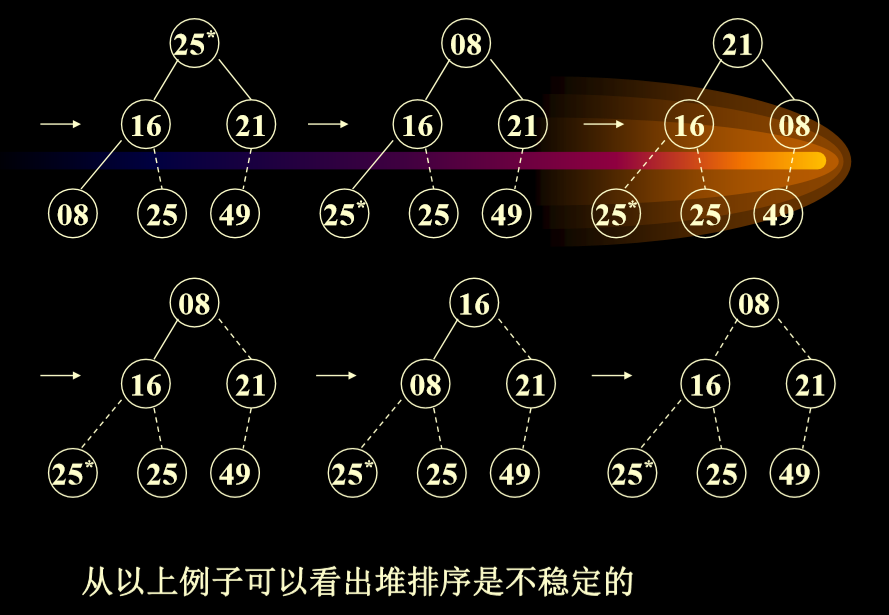
- 堆排序是不稳定的:因为相同数据的位置不同
- 堆排序每次删除最大的,然后把最大的放到最下方节点,把节点交换到顶部后进行下滤算法。
1 | |
1 | |
4.2. The Selection Problem 查找问题
- 问题描述:在N个元素中找出第K个最大元素。
- 1A算法:读入N个元素放入数组, 并将其选择排序,返回适当的元素。算法时间复杂度:O( N2)
- 1B算法:
- 将K个元素读入数组,并对其排序(按递减次序)。最小者在第K个位置上。
- 一个一个地处理其余元素:每读入一个元素与数组中第K个元素(在K个元素中为最小)比较,如果大于,则删除第K个元素,再将该元素放在合适的位置上(调整过程)。如果小于, 则舍弃。最后在数组K位置上的就是第K个最大元素。
- 运行时间(1B 算法): O(K2 + (N - K)K ) = O( NK ) 当 K = N / 2(向上取整), O( N2 )
- 例如:3, 5, 8, 9, 1, 10,找第3个最大元素。
4.2.1. 用堆来解决当前问题
- 6A算法:假设求第K个最小元素
- 将N个元素建堆(最小)O( N )
- 执行K次delete,O( K*logN ) O( N + K * log N )
- 如果 K = (N/2)(向上取整),O( N * log N )
- 如果 K = N ,O( N * log N ) 堆排序
- 如果是N取代最后一个是nlgn,可以考虑使用不同的情况来确定建立最大堆还是最小堆。
- 6B算法:假设求第K个最大元素
- 读入前K个元素, 建立最小堆O( K )
- 其余元素一一读入:每读入一个元素与堆中第K个最大元素比(实际上是堆中最小元素)O(1)
- 大于,则将小元素去掉(堆顶),该元素进入,进行一次调整。O(log K )
- 小于,则舍弃。
- O( K + ( N-K) * log K ) = O( N*log K)
- 当 K = (N/2)(向上取整) , θ(N * log N )
- 对6A, 6B,用同样的数据进行测试, 只需几秒钟左右给出问题解。
5. 例题:2009统考题

- 答案:A
- 直接按照顺序一行一行生成。
2019-数据结构-数据结构6.0-优先级队列
https://spricoder.github.io/2020/01/17/2019-Data-Structure/2019-Data-Structure-%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%846.0-%E4%BC%98%E5%85%88%E7%BA%A7%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97/