2019-计算机组织与结构-lecture12
Virtual Memory
1. 内存管理
- In the past, only OS and one program are in memory(过去只有操作系统和一个程序会使用内存)
- Currently, OS and multiple programs are in memory(现在,操作系统和多个程序使用内存)
- To avoid the idle of processor when the programs wait for I/O, it requires to load more programs in memory(为了避免程序在等待I/O的时候的处理器的空闲,处理器需要加载很多的程序进入内存)
- Memory management(内存管理)
- In multiprogramming system, the “user part” of memory should be further partitioned to fit multiple programs, which is dynamically carried out by OS(在多道程序设计系统中,内存的"用户部分"需要进一步划分以适应由操作系统动态执行的多个程序)
- Don’t consider “process” in this slide(在本节中不要考虑"过程")
2. 加载更多程序的解决方案
- Enlarge memory(增大内存)
- Using exchange and overlap techniques(使用交换和重叠技术)
- When no program is ready, OS loads other programs in(如果一个程序还没有准备好,操作系统加载另一个程序进来)
- Partitioning and paging(分区和分页)
- Virtual memory(虚拟内存)
- Demand paging(按需分页)
- Virtual address(虚拟地址)
3. 分区(Partitioning)
- 什么是分区?
3.1. Fixed-size partition(确定的分区策略)
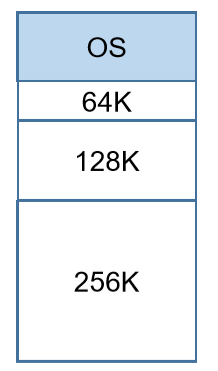
- OS: fixed size(确定大小)
- User program: fixed size with different lengths(确定的不同长度的程序)
- When load a program, put it in the smallest partition which has enough length(当加载一个程序的时候,把这个程序加载进入长度足够的最小的页里)
- Drawback(缺点): waste of memory(浪费内存)
- 操作系统如何分配分区?(重要)
- 选择一个目前是空的
- 能够放的下的
- 最小的
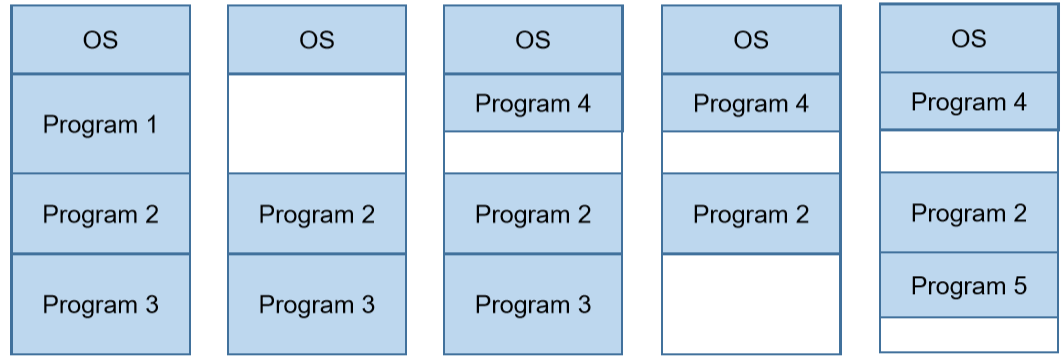
3.2. Variable-length partition(可变长的分区策略)
- OS: fixed size(操作系统:定长)
- User program: as requirement(用户程序:按需)
- Drawback: the number of fragments increases
(碎片数量会增加)
4. 分页(Paging)
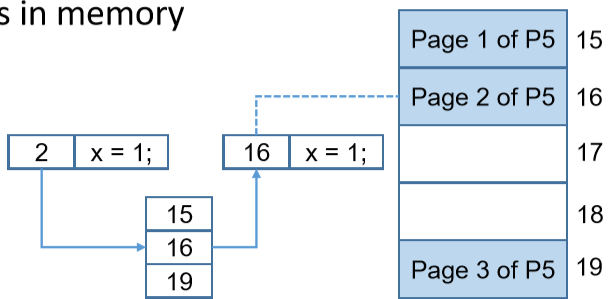
- Basic idea
- Divide the memory into fixed-size blocks, named page frame, and divide the program into fixed size blocks, named page(将内存分为一个个叫做页框的固定长度的块,然后将程序分为可以放进块的叫做页的部分)
- Load the pages into page frames(把页加载到页框里去)
- Logical address: address in instruction(逻辑地址:指令中的地址)
- Physical address: address in memory(物理地址:内存中的地址)
- 程序叫做页,放程序的地点叫做页框
- 页放在哪里由OS决定,在我们的程序中写的是逻辑地址,由操作系统的决定物理地址。
- 页放进去并不是连续的放入,记录页存在的位置
- 分页:将内存分成固定大小的页框,将需要存储成页,寻找空的页框放入(空的即可,因为一样大),这样做会导致程序的不连续性,但是有页表来记录地址。
5. Virtual Memory(虚拟内存)
- Problem
- The size of memory is limited, but the requirement of memory keeps increasing(内存的大小是有限的,但是对于内存的需求在不断的增加)
- Basic idea
- Demand paging: only load the active pages in paging(按需分页:只需要加载目前活跃的页)
- 用不到页就暂时不放进来。
- Essence(本质)
- Programming in a logical address space larger than memory(在大于内存空间的逻辑空间进行编程)
- Only load the required programs and data in memory(只在内存中加载需要的程序和数据)
- Transfer the logical address to physical address by hardware(通过硬件来转换逻辑地址成物理地址)
- Exchange information between memory and hard disk when miss(当发生了未命中的时候,我们在内存和硬件之间交换信息)
5.1. 虚拟内存示例
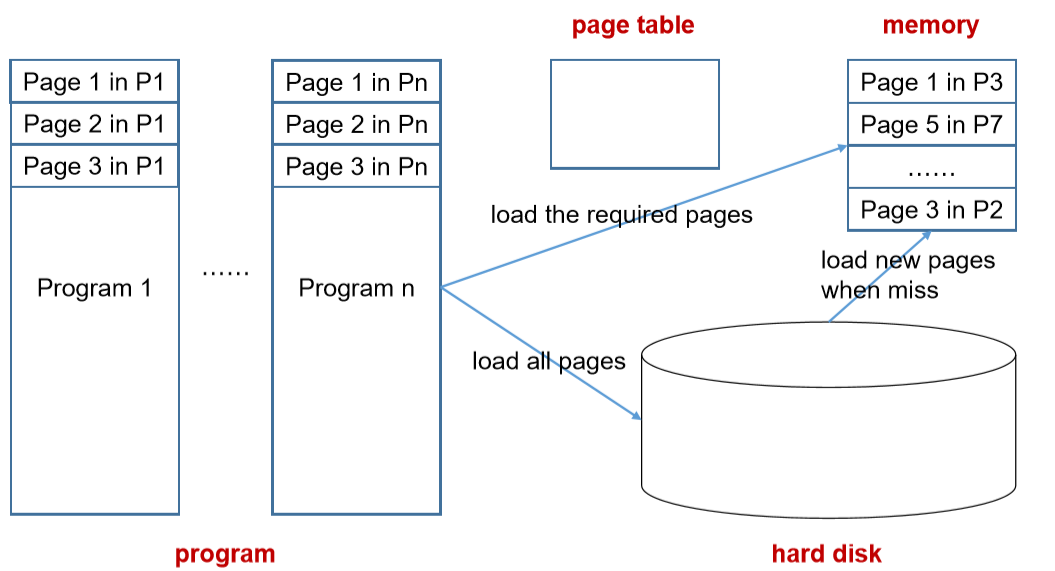
- 先把程序加载到硬盘的特定区域,然后我们什么时候需要这个内存,我们移动到memory中去。
- 存储是否被加载到物理内存中,如果被加载进入物理内存,则是物理地址。如果没有在里面则在Disk中
- 如果已经满了,我们就使用替换策略进行替换。
- 内存中有的,Disk中也是有的,因为是拷贝关系
5.2. 虚拟内存问题
- Size of page
- 4KB, 8KB, …
- Mapping function(映射方式)
- Associative mapping(全相联映射)
- Types
- Page based virtual memory(基于分页的虚拟内存)
- Segment based virtual memory(基于分段的虚拟内存)
- Segment and page based virtual memory(基于分段和分页的虚拟内存)
- Write policy
- Write back(写回策略),直到被替换出来才修改Disk中的数据
- 速度比例:
- Cache is 10 times faster than memory
- Memory is 100000 times faster than hard disk
5.2.1. Page based Virtual Memory(基于分页的虚拟内存)
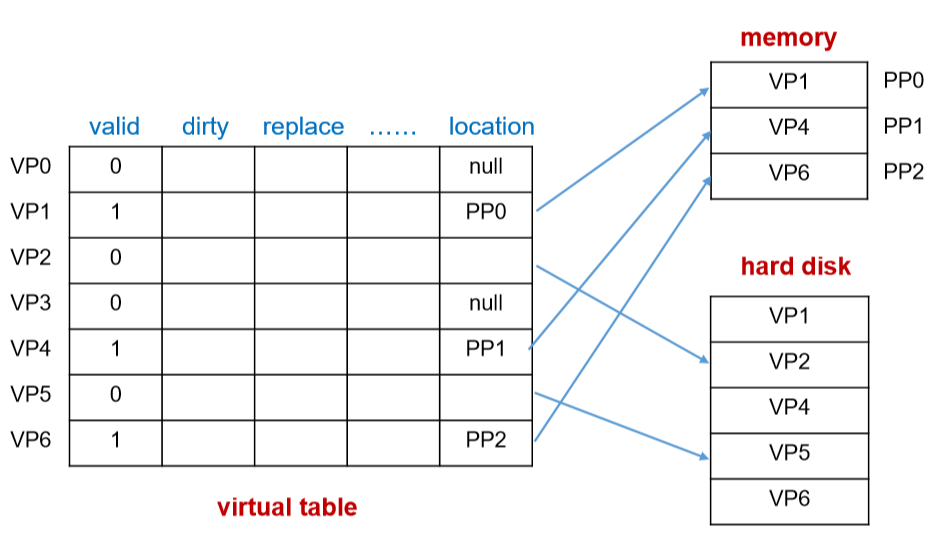
- Divide the main memory and virtual memory into pages with the same size(把主存和虚拟内存分成相同大小的页)
- Virtual page (VP) / logical page: page in virtual memory(虚拟页,简称虚页)
- Physical page (PP) / page frame: page in main memory(物理页,又叫页框)
- Page table(页表)
- A table contains the information of all VPs, including location(地址), valid bit(有效位,是否被加载到物理页中), dirty bit(脏位), r/w right et al.(页表中包含了所有的虚页,无论是否加载到主存中,都在页表中)
- Store in main memory(存在主存中)
- Virtual address(虚拟地址)
- Virtual page number + offset in page(虚拟页的页号+页内偏移)
- 每一个条目(虚拟页中):位置信息(物理页号、指向硬盘指针、null表示还没有被使用)、脏位(减少对磁盘的访问)、有效位(有无被加载到物理内存中)、读写权限
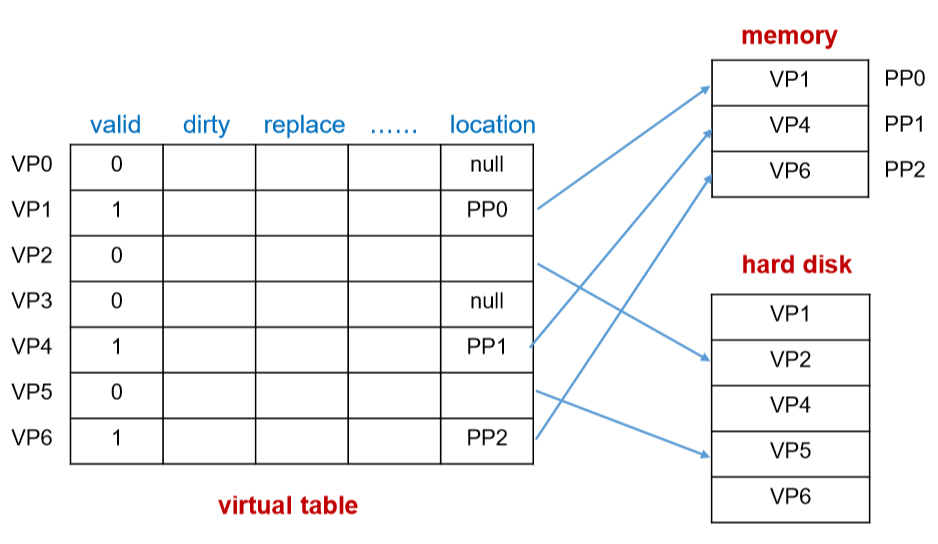
- 如上是一个页表的实现
- 如果虚页已经载入到了物理内存中,我们就要记录它的物理地址(location,valid = 1)
- location没写的存储的是指向硬盘(虚拟内存中)的指针
- location == null:表示磁盘里面没有,而不是内存中没有
- 虚拟页号比物理页号要大一些,虚拟页号没必要存储,按照相应的物理页号位置来找虚拟页号的位置
- 如果location的长度是不同的(null,物理页号,指针)
- 我们必须按照最长的部分来等长存储,以免无法进行更换
- 可以把页表放置到Cache中(但是是放置比较常用的页表的行)
- 页式的虚拟内存比分页好在哪里?
- 程序员不需要考虑具体存储的物理地址。
- 程序员可以有一个独享的大的内存。
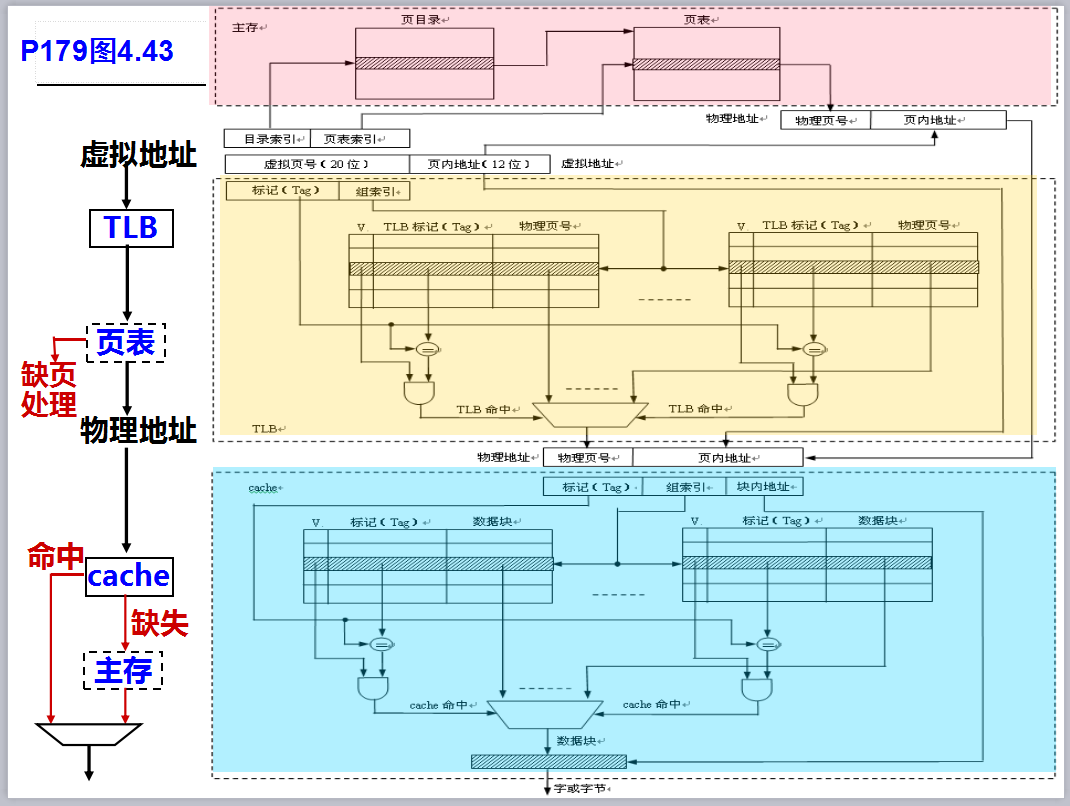
5.2.2. Translation Lookaside Buffer(快表,TLB)
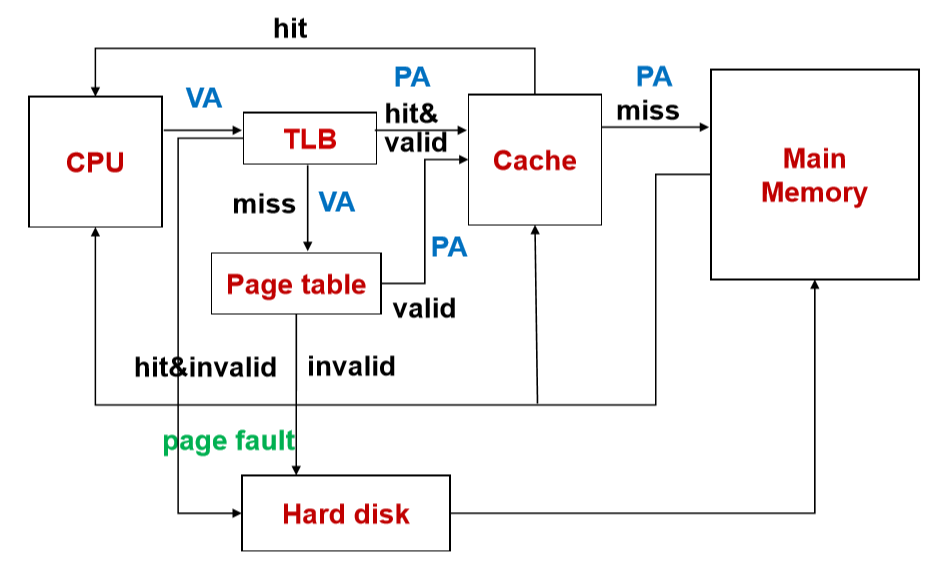
-
The usage of page table increases the access of main memory(页表的使用增加了对主存的访问)
-
To reduce memory access, load the frequently used items in page table to cache(为了去减少对内存的访问,我们将常用的页表的行放置到cache中去,需要在前面加上一个标记表示第几行)
-
TLB: the page table items loaded in cache(加载到cache中的页表)
- Associative mapping, set associative mapping(常用全相联映射和组相联映射)
- Random replacement(随机替换策略)
-
快表的实现流程图
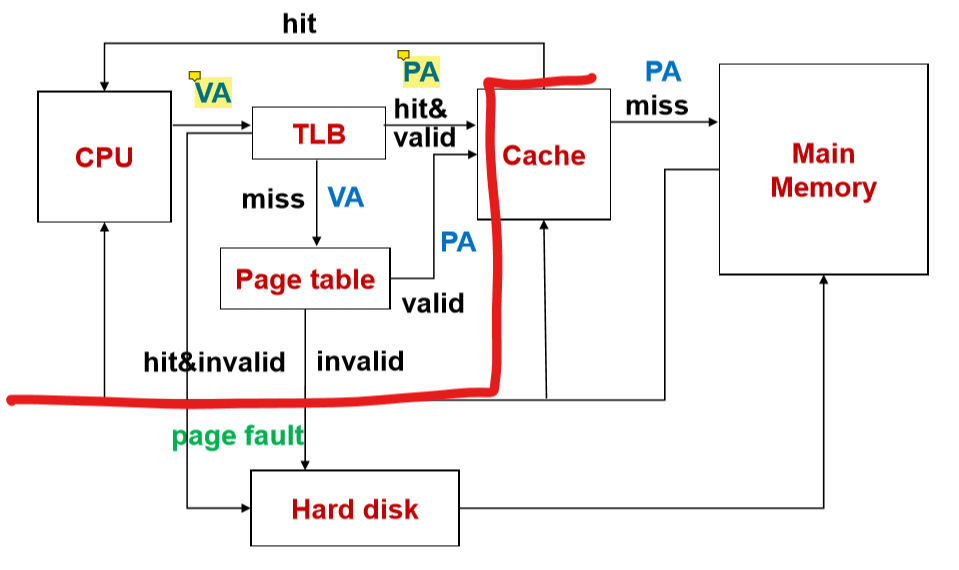
- 我们只要将虚拟页号(VA)根据页表(Page table)转换到物理页号(PA)中去
- 前提:在物理内存中:如果hit的话,直接传入物理地址。如果miss的话,我们到页表中去访问
- 如果hit并且是invalid的情况下,我们用硬盘把页送到内存中去,然后到cache正常访问。
- 如果未在物理内存中的话,也就是发生了缺页操作,于是对于磁盘(虚拟内存)进行操作。(也就是invalid的状态)

- cache是内存的拷贝
- TLB miss的情况下只是比hit的情况多一次内存访问
- TLB、页表valid表示在内存中
5.2.3. Segment based Virtual Memory(基于分段的虚拟内存)
- Divide the program and data into segments with different lengths, and load the required segments into memory(将程序和数据分成不同长度的段,并将所需的段加载到内存中)
- Virtual address(虚拟地址)
- Segment number + offset in segment(虚拟的段的地址 + 段内的偏移量)
- Compared to page base virtual memory(和基于分页的虚拟内存的对比)
- Page base virtual memory(基于分页的虚拟内存)
- Advantage: simple, low cost(简单,代价低)
- Disadvantage: instruction and data may cross pages(指令和数据可能会跨页)
- Segment based virtual memory(基于分段的虚拟内存)
- Advantage: naturally divide program and data(自然地划分程序和数据)
- Disadvantage: not fixed length(长度不确定)
- Page base virtual memory(基于分页的虚拟内存)
5.2.4. Segment and Page based Virtual Memory(基于分段和分页的虚拟内存)
- Divide the program and data into segments, and further divide the segments into pages(将程序和数据分段,然后将每一段在分到每一个页中去)
- Each segment has its page table(每一个段都有自己的页表)
- Virtual address(虚拟内存)
- Segment number + page number + offset in page(段号+页号+页内偏移量)
- Advantage
- Program is shared and protected in segment(程序被保护和分开在段内)
- Disadvantage
- Required multiple times table search(需要使用很多次表来进行搜素)
6. 编程作业的一些概念
- 实模式:没有使用虚拟内存。(效率高)
- 也就是给你的地址就是实际地址。
- 段:是一个虚拟内存
- 段内是有权限的保护。
- 访问页的时候是一样大的,但是访问段的时候是可大可小的。
- 段是由越界风险的。
- 段是起始位置(base)+长度(length),如果出现越界,则按照异常来进行处理
- 具体要读的位置是base+偏移量
- 段页式:
- 把本来连续的段拆成几个页。
- 也就是要为每一个段建一个页表。
- 也就是有段表和每一个段的页表。
2019-计算机组织与结构-lecture12
https://spricoder.github.io/2020/01/16/2019-COA19/2019-COA19-lecture12/