40-Spring Bean
spring Bean
- 本文简单记录了关于Spring中的Bean的实现和使用的部分理解
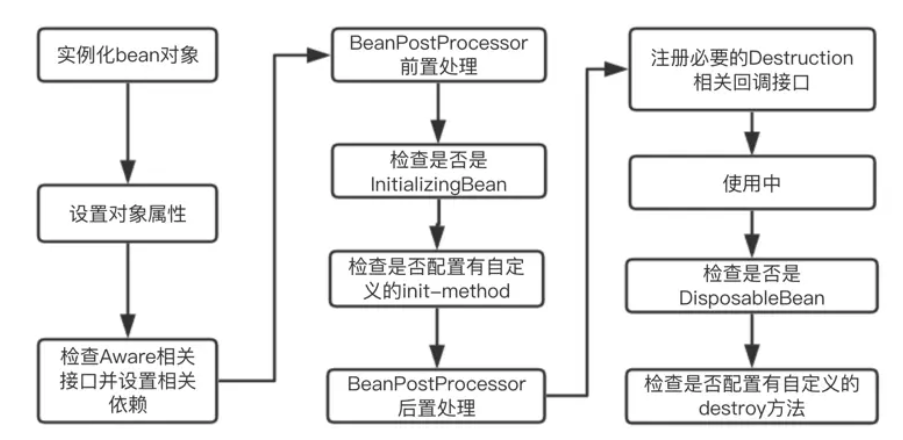
1. Spring Bean的简单流程
- 实例化【IOC容器寻找Bean的定义信息并将其实例化】
- 设置bean的Aware 【Aware意指能提前感知的,是spring的一个重要接口,使用依赖注入,spring按照Bean定义信息配置Bean的所有属性】
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)【如果BeanPostProcessor和Bean关联,那么其postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法将被调用,Spring 框架会遍历得到容器中所有的 BeanPostProcessor ,挨个执行】
- InitializingBean.afterPorpertiesSet 【初始化bean, springboot读取properties文件的过程,默认的application.properties 还有其他方式】
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 【如果有BeanPostProcessor和Bean关联,那么其postProcessAfterInitialization()方法将被调用】
- SmartInitializingSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated
- martLifecycle.start
- 运行Bean
- SmartLifecycle.stop(Runnable callback)
- DisposableBean.destroy()【销毁】
2. bean生命周期内的部分实现
2.1. 动态注入bean的思路
BeanFactory是 Spring 管理 bean 的对象- 具体是:
DefaultListableBeanFactory,这个类中有注入Bean的方法:registerBeanDefinition,在调用这个方法的时候,需要BeanDefinition参数 BeanDefinition的参数是通过BeanDefinitionBuilder来进行构建。
- 具体是:
- 所以我们动态注入bean的时候,只需要通过
ApplicationContext对象即获取到上BeanFactory。
2.2. 实现动态注入的代码
1 | |
2.3. 多次注入同一个bean的情况
- 如果同时注入到同一个bean中,如果beanName不同的话,那么就会产生两个Bean,如果beanName一直的话,后面注入的会覆盖前面的。
1 | |
2.4. 设置Bean的Aware
InitializingBean.afterPorpertiesSet,BeanPostProcessor对bean的加工处理基本上在一块出现。- 设置Aware方法顺序:
- BeanNameAware
- BeanClassLoaderAware
- BeanFactoryAware
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor也会设置Aware:- EnvironmentAware
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware
- ResourceLoaderAware
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware
- MessageSourceAware
- ApplicationContextAware
1 | |
2.4.1. SmartInitializingSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated的调用位置
1 | |
2.4.2. SmartLifecycle.start
- 在ApplicationContext结束刷新finishRefresh时,getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
- 判断bean是否为SmartLifecycle并且autoStartup。
- 位于:DefaultLifecycleProcessor.onRefresh
2.4.3. stop方法
- 在Application.close的时候,调用getLifecycleProcessor().stop()方法仍然在DefaultLifecycleProcessor内部
2.4.4. DisposableBean.destroy方法
- doCreateBean方法中会判断bean是否有销毁相关操作,实现了DisposableBean方法或定义了销毁方法。
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
Bean声明周期演示以及运行结果
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
2.5. 动态删除Bean
1 | |
3. 参考
40-Spring Bean
https://spricoder.github.io/2022/04/13/Spring-Boot/40-Spring-Bean/