2021-数据库开发-Lec4-SQL优化
Lec4-SQL优化
1. SQL优化
1.1. 关系代数
- E.FCodd关系理论之父,关系代数究竟有什么用?
- 代数是表达式的等价变换
- 关系代数也是一样
- 2、3、4 这些数字对应的就是 关系(表)
- ±×/ 这些运算符对应的就是 关系操作
- 如果将所有的路径全部遍历完会有比较大的代价,同时还要对知识、应用环境的现在、未来、时间空间分布有了解。

1.2. 关系代数使数据库变成了科学而不是艺术
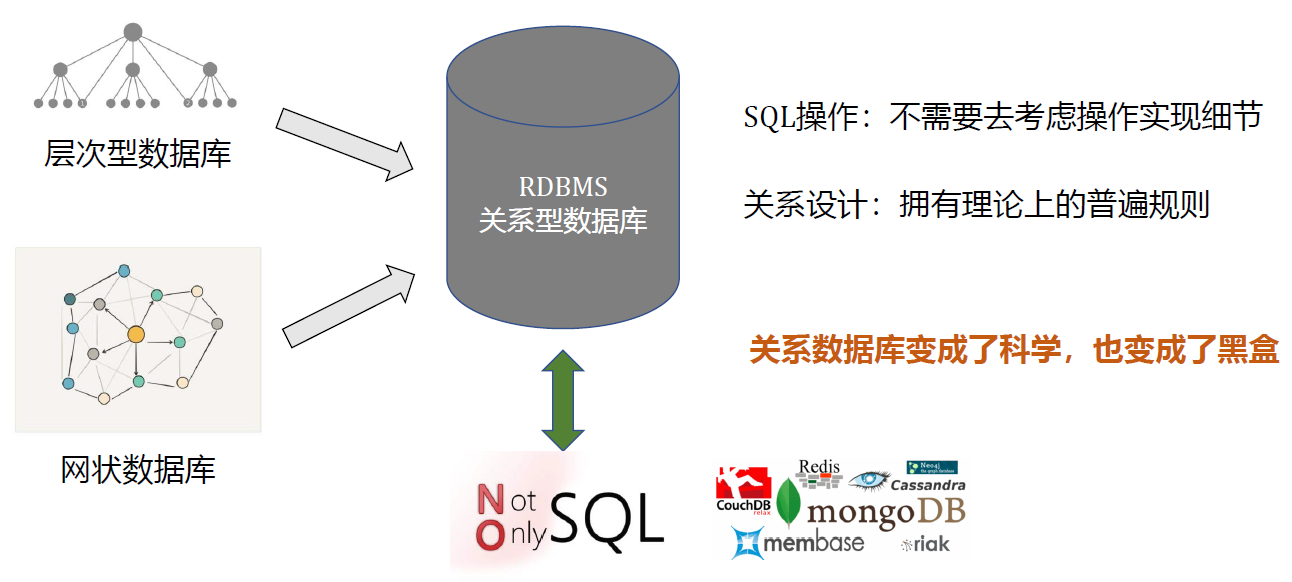
查询优化器完成具体查询的优化
1.3. SQL与查询优化器
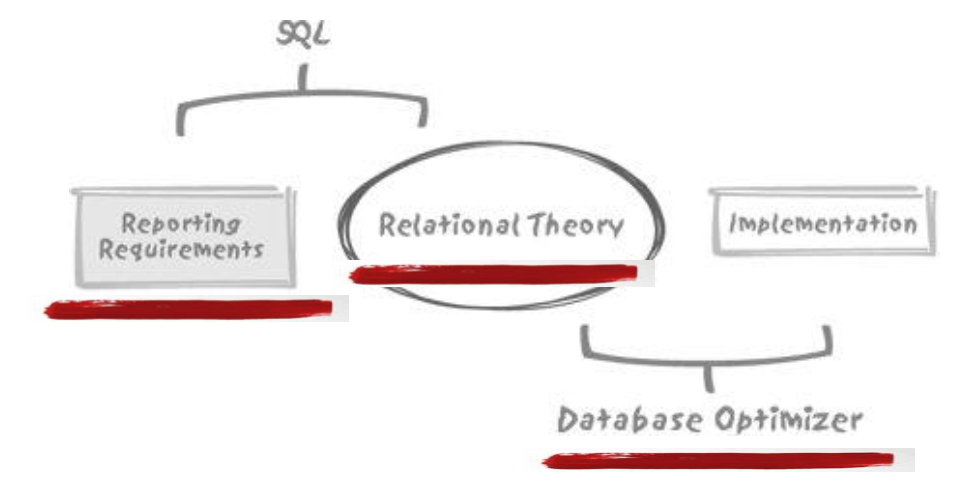
- 优化器借助关系理论提供的语义无误的原始查询进行有效的等价变换,优化在发生查询的时候才发生。
- 优化器根据数据库的实际实现情况对理论上等价的不同优化方案做出权衡
- 产生可能的最优查询执行方案
- 排序、统计等不是在关系代数中完成的,而是在SQL中完成的。
1.4. SQL的执行顺序
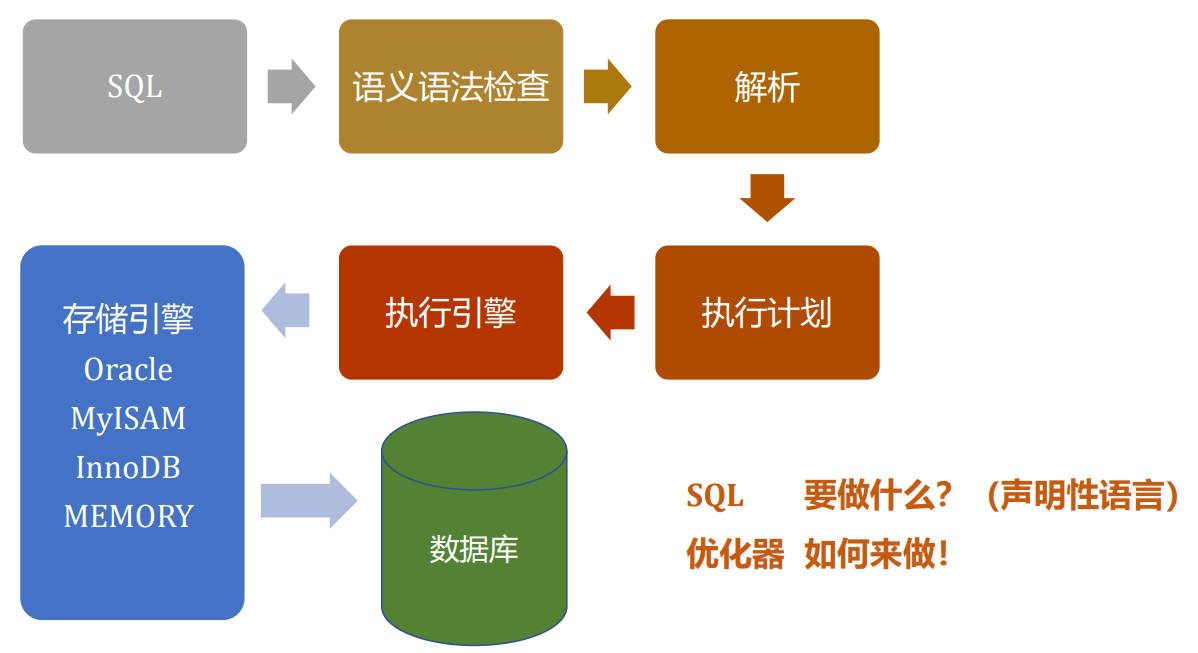
- SQL语句首先通过语义和语法检查,进入查询环节,进行解析,是整个SQL优化最消耗资源的环节。
- 之后对于每一个表达式的等价变化生成解析树,然后进行评估。由优化器选择一个最满意的执行路径来生成执行计划(plan和二进制的执行代码)
- 将执行计划导入到执行引擎后在数据库中进行查询。
- 查询优化器不能检查SQL本身的错误
- 查询优化器不能优化中间结果集
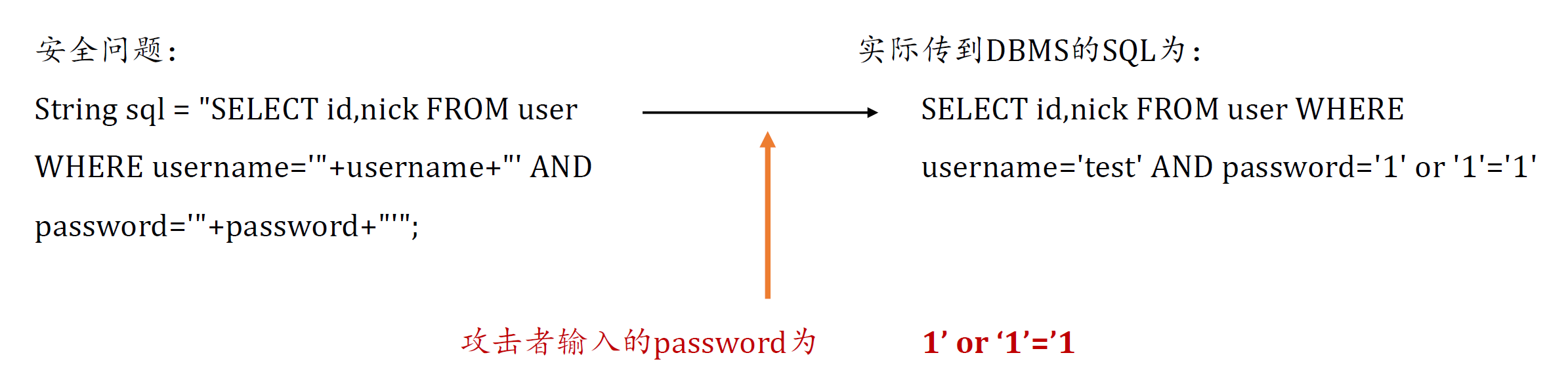
- 软解析的问题:目前主流的还是采用硬解析的方式,尽量避免出现SQL注入的问题
1.6. 优化器只能对关系领域进行优化
- 忽略这点很可能出现错误
- 例子:查询不是经理的员工当中,哪五个人收入最高?注意order by的问题
1 | |
1.7. 优化器的有效范围
- 优化器需要借助数据库中找到的信息
- 能够进行数学意义上的等价变换
- 优化器考虑整体响应时间:复杂查询可能无法优化的很好
- 优化器改善的是独立的查询
1.8. 思考题
- Oracle的rownum是一个非常讨厌的SQL方言,但它是Oracle数据库中唯一的限定返回行数的函数,其它数据库也有类似的方言
- DB2使用FETCH FIRST子句
- MySQL和PostgreSQL使用LIMIT子句
- SQL Server使用TOP关键字
- 请你用你手上常用的数据库试一下本课程那个限定返回行数查询的例子,看看有没有Oracle出现的问题
- 如果你是用Oracle,你试一下,你能通过rownum=5,来返回第5行记录嘛?
2. 使用SQL需要考虑的因素
- 获得结果集所需访问的数据量
- 定义结果集所需的查询条件
- 结果集的大小
- 获得结果集所涉及的表的数量
- 同时修改这些数据用户的多少
2.1. 数据总量
- SQL考虑最重要因素:必须访问的数据总量
- 没有确定目标容量之前,很难断定查询执行的效率
2.2. 定义结果集的查询条件
- Where子句,特别在子查询或视图中可能有多个where子句
- 过滤条件的效率有高有低,受到其他因素的影响很大
- 影响因素:过滤条件、主要SQL语句、庞大的数据量对查询的影响
- 对于过滤条件而言,我们需要考虑两个条件:一个是80%的行满足,一个是10%的行满足,那么我们先做哪个,那么肯定优先是第二个的
- 分页拆分是很好的方法
2.3. 结果集的大小
- 查询所返回的数据量,重要而被忽略:考虑用户体验,比如2s的查询后没有结果
- 取决于表的大小和过滤条件的细节
- 例外是若干个独立使用效率不高的条件结合起来效率非常高
- 从技术角度来看,查询结果集的大小并不重要,重要的是用户的感觉
- 熟练的开发者应该努力使响应时间与返回的记录数成比例
2.4. 表的数量
- 表的数量会对性能有影响
- 表的join连接
- (太)多表连接该质疑设计的正确性了
- 对于优化器,随着表数量的增加,复杂度将呈指数增长。
- 编写(太)多表的复杂查询时,多种方式连接的选择失误的几率很高
- 代码表:往往是供查询和下拉菜单的
- 对于有多个外键的表,不存储eid,而选择名称之类的,但是容易导致不一致性问题,这就意味着我们不能允许用户自由输入而是通过选择的方式输入。
- 还有一个容易忽视的问题,复杂查询和复杂视图:基本的原则是,当是视图返回的数据远多于上级查询所需要的时候,就放弃使用该视图
- 能不使用视图就不使用视图,视图会屏蔽很多优化细节
2.5. 并发用户数
- 设计的时候需要注意
- 数据块访问争用(block-access contention)
- 阻塞(locking)
- 闩定(latching)
- 保证读取一致性(read consistency)
- 一般而言,整体吞吐量>个体响应时间
2.6. 思考题
- 你还有什么方法(自己遇到的,或者查询技术资料、论坛等等资源)能够在数据库应用方面,照顾好用户的情绪?欢迎你的分享。
3. SQL过滤的条件
3.1. 查询的过滤条件
- 如何限定结果集是最为关键的因素
- 也是使用SQL各种技巧的判断因素
3.2. 过滤条件的含义
- Where子句和having子
- Join过滤条件
- Select过滤条件
1 | |
- 假设有一个参数表 p(pname,ptype,pvalue)无论ptype定义了什么参数属性,pvalue都是用字符串表示(请记住这是一个错误的用法)
1 | |
3.3. 过滤条件的好坏
- 最终需要的数据是什么,来自哪些表
- 哪些输入值会传递到DBMS引擎
- 能过滤掉不想要的数据的条件有哪些
- 高效过滤条件是查询的主要驱动力
3.4. 来,去买BMW
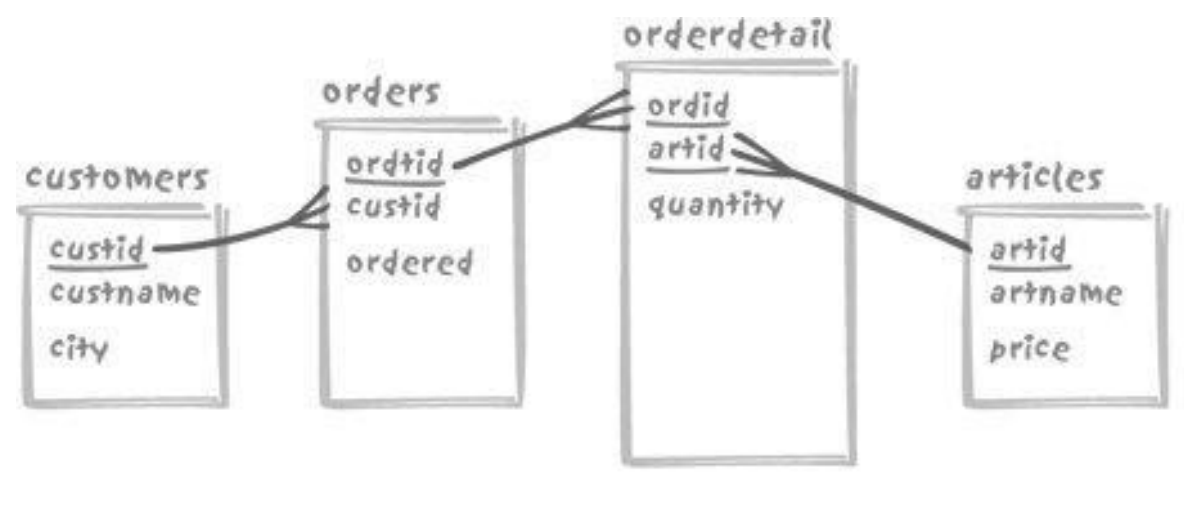
- 找出最近6个月住在nanjing,购买了BMW的所有客户
- 按照下面的方式先连接再使用条件查询的方式会避免遗漏
1 | |
- 古老的自然连接方式:性能会很差(系统不会很复杂),避免在最高层出现distinct
1 | |
3.5. 进一步
- 避免在最高层distinct应该是一条基本规则
- 发现重复数据容易,发现不准确的连接难
- 发现结果不正确就更难了
3.6. 摆脱distinct的方法
- 客户在Nanjing市,而且满足Exists存在性测试即在最近六个月买了BMW
1 | |
3.7. 非关联子查询
1 | |
- 关联子查询中,orders表中custid字段要有索引,而对非关联子查询则不需要,因为要用到的索引是customers的主键索引
- 内层查询不再依赖外层查询,只需要执行一次
3.8. 还可以进一步嵌套
- exists -> ordid in
1 | |
3.9. 还没看够不同的SQL写法嘛?
- 对于很多数据库来说,非关联子查询还可以写成from子句的内嵌视图
1 | |
3.10. 跟我去买BMW例子的总结
- 找到分辨率最强的条件
- 解决方案不止一种,查询和数据隐含的假设密切相关
- 预先考虑优化器的工作,以确定它能找到所需要的数据
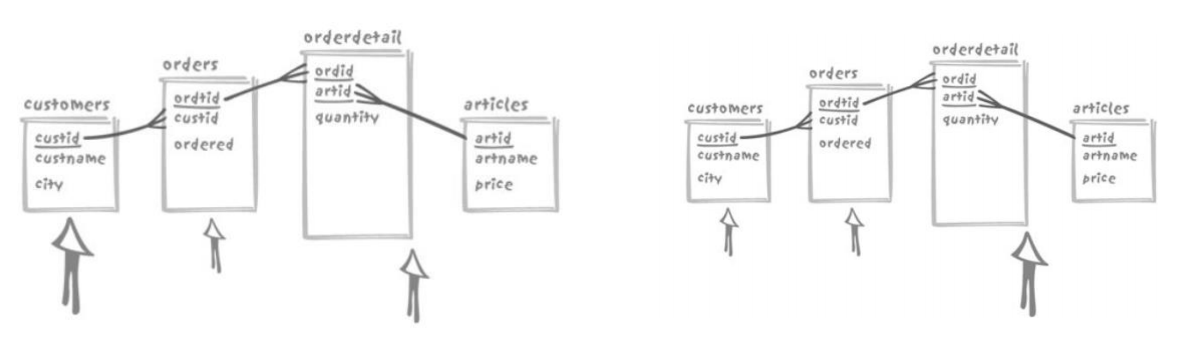
3.11. 多表关联的不同优化器的策略
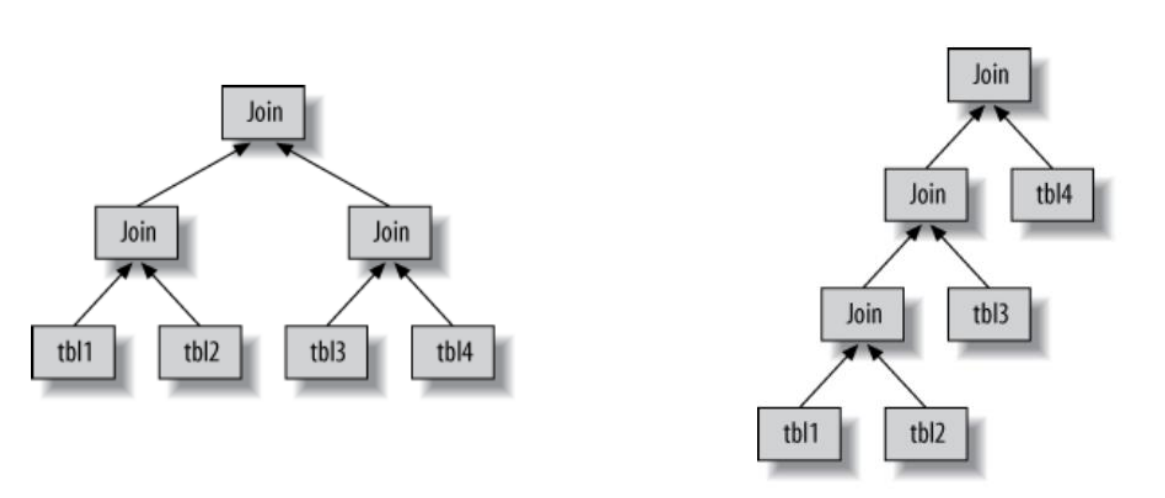
3.12. 思考题
- 你可以比较两个查询,在MySQL的Sakila示例数据库中分析不同查询的差异
1 | |
- 使用EXPLAIN命令查询执行计划和执行时间,分析一下性能差异的原因
4. 改写SQL降低表连接
4.1. where子句的比较运算符
- select中的函数只计算一次,而where中的函数要计算多次
1 | |
- 请看下面这个例子,分析3条SQL语句的差别
1 | |
- 创建一个40万+的表
- 统计3条SQL语句的差别,都是统计2019年4月20日这一天每个用户下的对象的个数
- 数据库底层文件堆文件,按块存储,一个块默认4K大小,如果本块的最后一条数据中,如果变长导致超出块长度则将这个记录的部分放在下一个块中(再存储一个链接),这种情况叫做行迁移。
- 数据一般只允许一次行迁移
- 如果要发生第二次行迁移,则将这条记录存放到单独的块中
- 下列的二使用不到索引,导致每一条要执行一次函数计算
- 下列的三使用不到索引,导致每一条要执行两次函数计算
- 慢查询和快查询:需要有大量的操作的情况下才会感受到
- 慢查询会拖累同系统内的快查询
1 | |
4.2. 比较运算符的转化
4.3. 大数据量查询
- 越快剔除不需要的数据,查询的后续阶段必须处理的数据量就越少,查询效率就越高
1 | |
4.4. 将子查询转换为JOIN
- 不包含聚合函数,不出现多种条件选择可以不需要子查询
- Jobs(employee,title) Ranks(title,rank)Salary(rank,payment)
1 | |
4.5. 查询不存在的内容(左右连接)
- 在salary表中查询是否存在某个等级当前没有分配职位,显示等级和薪水
- Jobs(employee,title) Ranks(title,rank)Salary(rank,payment)
1 | |
4.6. 将聚合子查询转换为JOIN或内嵌视图
- 在订单完成前有不同状态,记录在orderstatus(ordid,status,statusdate)中
- 需求是:列出所有尚未标记为完成状态的订单的下列字段:订单号,客户名,订单的最后状态,以及设置状态的时间。
4.7. 再回头看订单和客户的例子
- 需求是:列出所有尚未标记为完成状态的订单的下列字段:订单号,客户名,订单的最后状态,以及设置状态的时间
1 | |
4.8. 非关联子查询变成内嵌视图
1 | |
4.9. 思考题
- Orders(custid,ordered,totalitems)
- 需要显示每一个客户购物件数最多的日期,如何用连接改写这个SQL的子查询
1 | |
5. SQL的主题
5.1. 字符串处理
- 遍历字符串
- 嵌入引号
- 统计字符出现的次数
- 删除不想要的字符
- 分离数字和字符数据
- 判断含有字母和数字的字符串
- 提取姓名的首字母
5.2. SQL的字符串处理
- SQL并不专门用于处理复杂的字符串
- 很多时候非常麻烦,令人沮丧
- BUT,仍然有很多很好用的内置函数
- 任何事物,包括SQL都有自己好的一面和坏的令人厌恶的一面
5.2.1. 遍历字符串
- 这是一切字符串处理的基础,你需要有逐字遍历字符串的能力
- SQL没有Loop循环功能,我们需要有数据透视表(T1,T10,T100…)
- 问题:把EMP表中的ENAME=KING的字符串拆开显示为4行,每行一个字符
1 | |


5.2.2. 嵌入引号
- 如果想在字符串常量中嵌入引号,并且希望使用SQL产生如下所示的结果
1 | |
5.2.3. 统计字符出现的次数
- 问题:统计字符串中有多少个逗号?10,CLARK,MANAGER
1 | |
- 问题:如何统计HELLO HELLO中出现了多少个LL
1 | |

- 除法运算是得到“次数”这类运算正确答案必须使用的运算手段
5.2.4. 删除不想要的字符
- 问题:从数据里删除指定的字符,从左边的结果集中的数据里删除所有的0和元音字母,并将删除后的值显示在STRIPPED1列和STRIPPED2列中,形成右边的结果集形态

- 先用TRANSLATE函数把元音字母替换成一个特殊的字符,然后使用REPLACE函数删除这个特殊字符
1 | |
- 没有TRANSLATE函数,那就只有做苦力活了
1 | |
5.2.5. 分离数字和字符数据
- 问题:把数据中的数字数据和字符数据分开,怎么办?
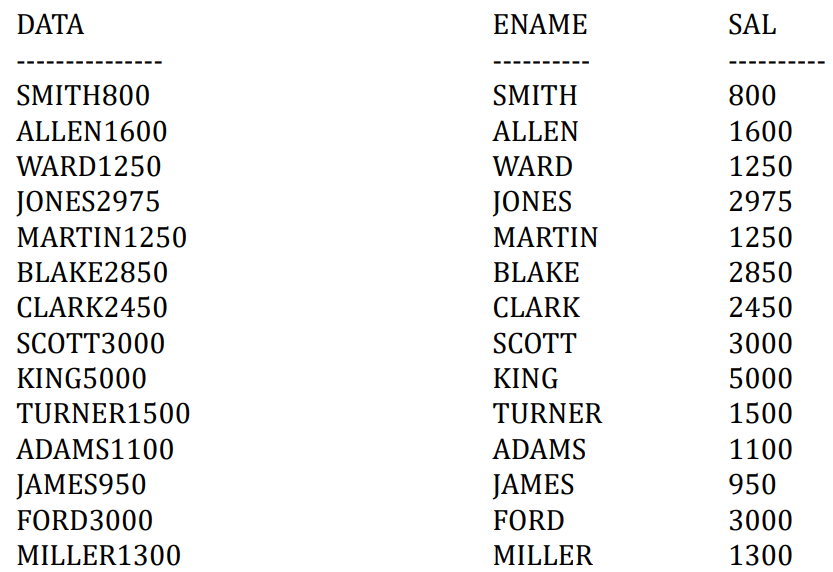
- MySQL只用REPLACE怎么办?
1 | |
5.2.6. 判断含有字母和数字的字符
- 问题:从表里筛选出部分行数据,筛选条件是只包含字母和数字字符
- 视图V

1 | |
5.2.7. 提取姓名的首字母
- 问题:你想把姓名变成首字母形式,比如LeBron James, 就可以变成L.J.
1 | |
5.2.8. 还有些字符串操作比较复杂
- 创建分隔列表、字段内部排序、解析IP地址等等
- 但一般很少使用,我们可以通过更好的设计避免出现这样的问题
- 但,SQL处理字符串的能力是非常弱小的,每个数据库都有自己的内置函数,且无法通用
5.2.9. 思考题
- 把行数据变成以某种符号分割符的列表,比如逗号
- 可以使用聚合函数完成的业务都不要到业务逻辑(前端和后端)来处理

5.3. 数值处理
5.3.1. 示例使用的相关表和数据
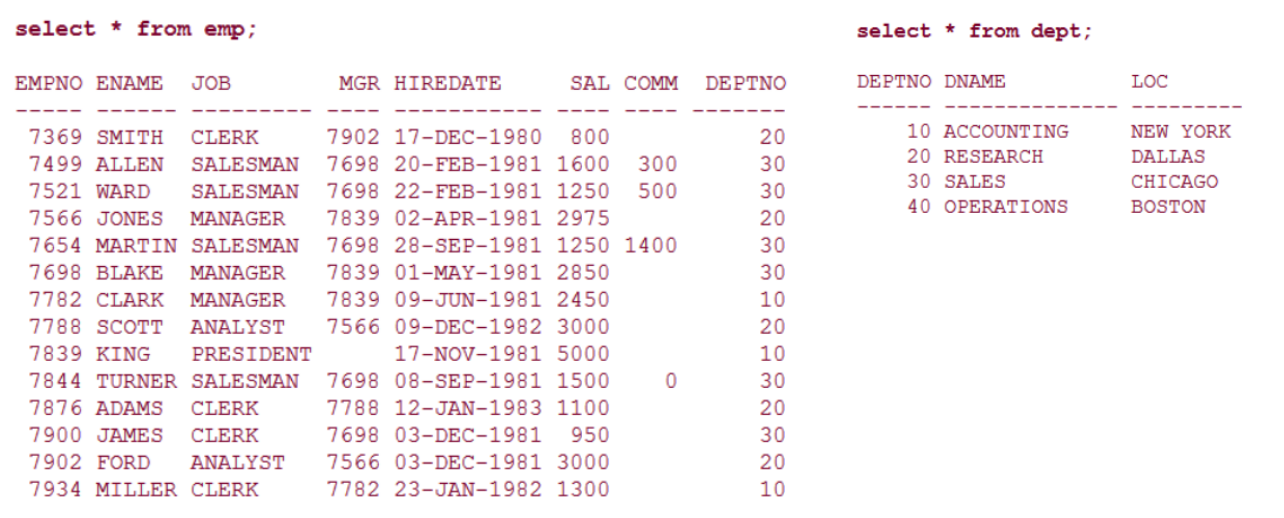
5.3.2. 计算平均值
1 | |
- 遇到空值怎么办?直接忽略空值
- 如果需要统计空值?
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
1 | |
5.3.3. 查找最大值和最小值
1 | |
5.3.4. 求和
1 | |
5.3.5. 计算行数
1 | |
1 | |
- 计算某一列的非空个数
1 | |
5.3.6. 累计求和(Running Total)
1 | |
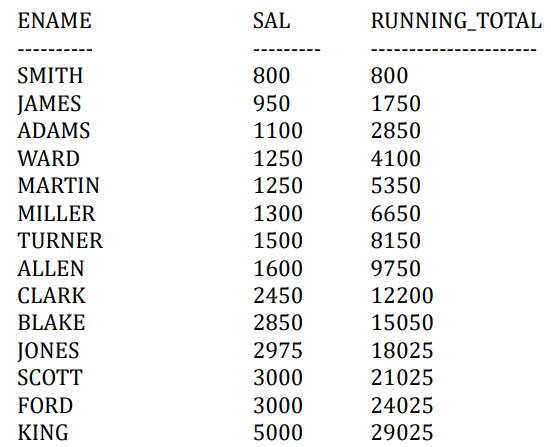
1 | |
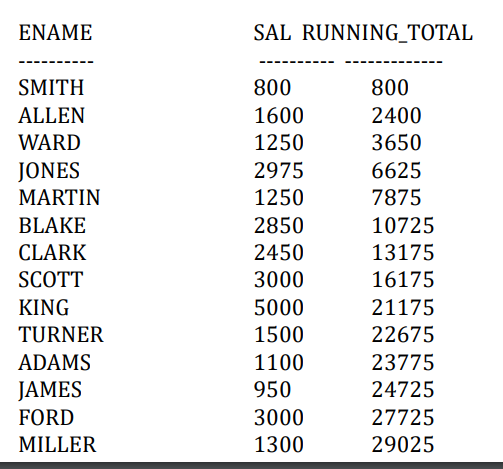
5.3.7. 计算众数
1 | |
1 | |
5.3.8. 计算中位数
1 | |
1 | |
- 表的自连接是很重要的一种手段
5.3.9. 计算百分比
1 | |
5.3.10. 计算平均值时去掉最大值和最小值
1 | |
5.3.11. 修改累计值
- 问题,你想依据另一列的值来修改累计值。有这样一个场景,你希望显示一个信用卡账户的交易历史,并显示每一笔交易完成后的余额。
1 | |
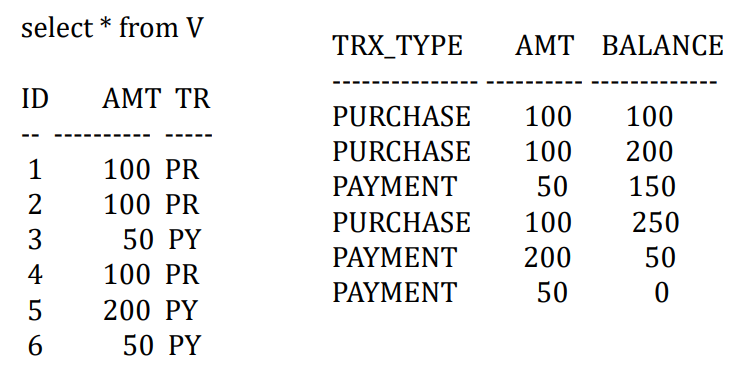
1 | |
5.3.12. 思考题
- 2.5是进行累加,你看看怎么做累计乘法,和累计减法。
- 如果有时间,希望你把这一讲中所有的例子在你的数据库中尝试一下
- 如果你还有时间,创建大一点的表,100万行,然后执行查询100次,1000次或者100个并发同时执行,就可以感受到性能和效率
- 尝试将读写分离来提高资源:可以先离线计算出一个中位数(但是不是完全正确,但是已经相当精确)
5.4. 日期处理
5.4.1. 年月日加减法
- 问题,以员工CLARK的hiredate为例,计算入职的前后五天,入职的前后五个月,以及入职前后5年的日期,hiredate=‘09-JUN-1981’
1 | |
5.4.2. 计算两个日期之间的天数
1 | |
5.4.3. 计算两个日期之间的工作日天数
1 | |
5.4.4. 计算当前记录和下一条记录之间的日期差
- 计算deptno=10的部门每一个员工入职时间相差多少天
1 | |
5.4.5. 判断闰年
1 | |
- CURRENT_DATE和CURRENT_DATE()是CURDATE)_的同义词。
5.4.6. 计算一年有多少天
期末考试有可能会考
1 | |
5.4.7. 找到当前月份的第一个和最后一个星期一
1 | |
5.4.8. 依据特定时间单位检索数据
- 指定月份、星期或者其它时间单位来筛选记录行。
- 比如:找到入职月份是February或者December,而且入职当天是星期二的所有员工
1 | |
5.4.9. 识别重叠的日期区间
1 | |
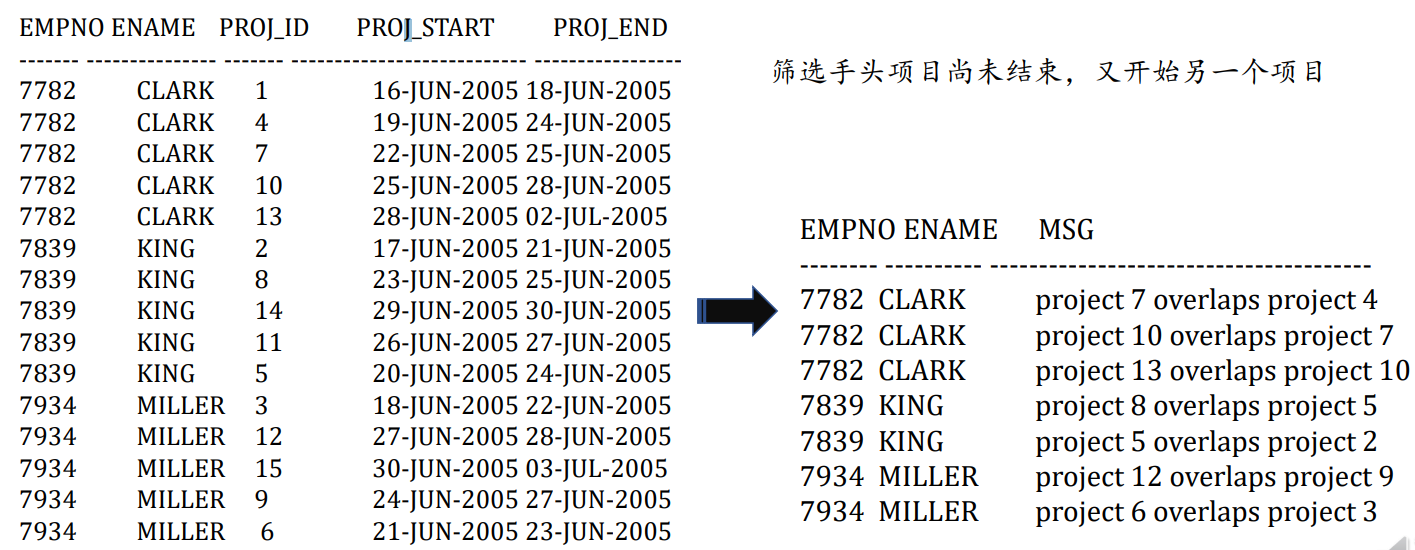
1 | |
5.4.10. 思考题
- SQL题目
- 找出当前季度的第一个星期天和最后一个星期三
- 计算两个日期差几个月,几年,比如17-dec-2017,和12-JAN-2020 ,不能直接2020-2017,因为实际他们只差了25个月,两年多一点点
- 找到同月同日的人
- 2,3两题,日期都是从数据库不同记录中读出的,是一个通用的SQL,比如这组例子,2是员工入职的最大值和最小值之间差多少,3比如找到入职的同月和同日的人
5.5. 常见SQL连接模式
5.5.1. 叠加行集(Union & Union all)
- 如果需要显示EMP表中部门ID等于10的信息以及DEPT表中各个部门的名称和编号
- 将不相关内容放到一个表中

1 | |
- 必须保证类型相同和字段数要相同
- 如果有重复内容UNION ALL一并纳入
1 | |
5.5.2. 查找只存在于一张表的数据(差 -)
- DEPT表中DEPTNO=40的数据并不存在于EMP表中,怎么把它找出来?
1 | |
- MySQL:空值not in会出现问题,同时避免in,改用exists
1 | |
5.5.3. 从一个表检索另一个表不相关的行(外连接)
1 | |
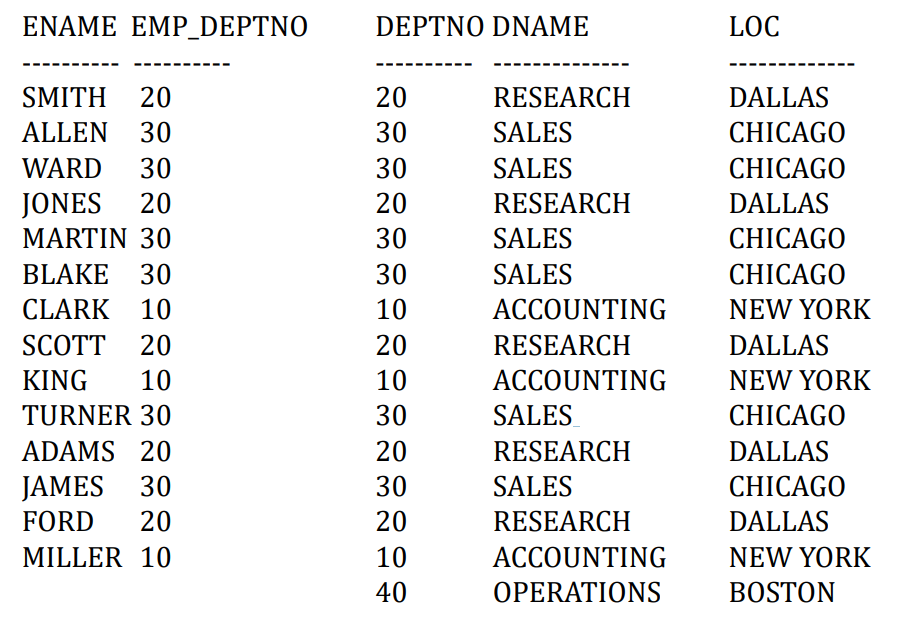
5.5.4. 确定两个表是否有相同的数据
- 问题:想知道两个表是否有相同的数据
1 | |
- 希望返回如下结果集
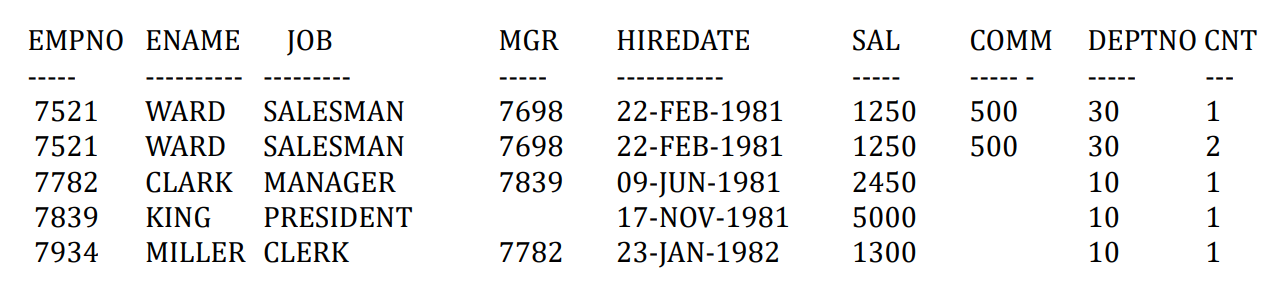
1 | |
5.5.5. 从多个表中返回缺失值(全外连接)
1 | |

5.5.6. 连接和聚合函数的使用
- 考虑新增一张bonus表,注意,存在重复记录
1 | |
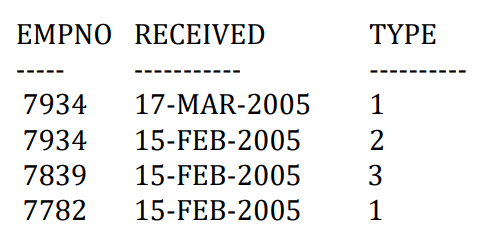
1 | |
1 | |
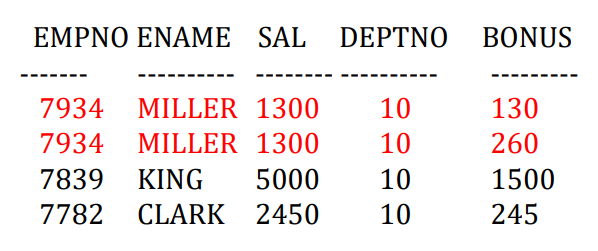
- 但是这个查询中,部门为10的所有人都有奖金
1 | |
5.5.7. 思考题
- 接4.6,修改了一个条件,不是所有员工都有奖金:少算也可能出问题
- 请计算出部门编号为10的员工的工资总额和奖金总额
1 | |

1 | |
2021-数据库开发-Lec4-SQL优化
https://spricoder.github.io/2021/05/02/2021-Database-Development/2021-Database-Development-Lec4-SQL%E4%BC%98%E5%8C%96/