2020-C++高级程序设计-C++ 输入输出
C++ 输入输出
1. I/O
- 输入输出流:包含在头文件
<iostream>中 - 开头需要进行
#include<iostream>
1.1. 标准库对象
| 对象 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| istream:cin | 处理输入 |
| ostream:cout | 处理输出 |
| ostream:cerr | 处理错误 |
| ostream:clog | 保证log |
2. 输入
2.1. 输入原理
- 程序的输入都键入一个缓冲区,即输入缓冲区。
- 键盘输入结束后,会将数据存入缓冲区,之后cin函数直接从输入缓冲区取数据
- 问题在于:缓冲区中有残留数据的时候,cin输入流直接从缓冲区拿数据。
2.2. cin
>>是流提取符,以空格,\t(Tab),\n(回车)为终止- 往往使用来赋值给变量
- cin的变量类型可以为int、float、char、char*、string等诸多类型。
2.2.1. 数组输入
1 | |
2.2.2. 解决格式化输入问题
1 | |
2.2.3. get方法
1 | |
- 结束符默认为enter,结束字符串的读写
- 字符串最后一个为
\0,并且对空格不敏感。 - get方法并不会将结束符从缓冲区丢弃:务必注意是结束符!未必是回车。
1 | |
- 直接回车在上面程序中会出现错误输出(越界),处理方法
cin.clear():但是不会清理终止符。
1 | |
2.2.4. cin.getline()
cin.getline(字符数组名,接收长度,结束符)- cin.get()超长后不会影响cin的操作,而cin.getline()如果超长会导致之后cin的错误。
2.2.5. getline()
getline(istream is,string str,结束符)
1 | |
2.3. cin异常处理机制
2.3.1. 标志位
- 定义在IOS类中
- 他们不是储存异常状态常量,而是对应状态为的掩码。
| 名称 | 二进制显示 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| failbit | 001 | 输入(输出)流出现致命错误,不可挽回 |
| eofbit | 010 | 已经到达文件尾 |
| badbit | 100 | 输入(输出)流出现非致命错误,可挽回 |
| goodbit | 000 | 流状态完全正常,各异常标志位都为0 |
1 | |
2.3.2. rdstate()
- rdstate():获取标志变量的值
1 | |
2.3.3. bool ios::fail()const
- 1 or true if rdstate & failbit is nonzero, otherwise 0 or false. (引用msdn)
- 其中rdstate即通过rdstate()取得的标识变量的值,与failbit相与,即取得failbit标志位的值,如果结果非零则放回true,否则返回false。即该函数返回failbit的状态,将标志位状态通过bool值返回。
2.3.4. bool ios::bad() const
- 1 or true if rdstate & badbit is nonzero; otherwise 0. (引用msdn)
与fail()相似。
2.3.5. bool ios::good()const
- 1 or true if rdstate == goodbit (no state flags are set), otherwise, 0 orfalse. (引用msdn)
改函数取goodbit的情况,即三个标志位都0(即没有任何异常情况)时返回true,否则返回false。
2.3.6. voidios::clear(iostate _State=goodbit)
- 该函数用来重置标识变量,_State是用来重置的值,默认为goodbit,即默认时将所有标志位清零。用户也可以传进参数,如:clear(failbit),这样就将标识变量置为failbit(即:001)。
- 我们一般是用它的默认值,当cin出现异常,我们用该函数将所有标志位重置。如果cin出现异常,没有重置标志的话没法执行下一次的cin操作。如上一节的程序2的测试二为什么第二次输入操作没有执行?程序8中 cin>>ch 为什么没有执行?都是这个原因!!!
所以经常在程序中使用 cin.clear(), 为了重置错误标志!
2.3.7. void ios::setstate(iostate_State)
- 这个函数也是用来设置标识变量的,但与clear()不同。clear()是将所有标志清零,在置以参数新的标志。而该函数不清零其他的标志,而只是将参数对应的标志位置位。这个函数不是经常使用,这里不再赘述。
2.3.8. 例子
1 | |
- 【分析】程序执行结束还是只执行了一次读操作,cin>>ch还是没有从键盘读取数据,但是与程序8中不同,这里打印了ch的值为’5’,而且在cin>>ch之前已经清楚了错误标志,也就是cin>>ch的读操作实际上执行了。这就是前面讲的cin读取数据的原理:它是直接从输入缓冲区中取数据的。此例中,第一次输入"12345",而getline(str, 5)根据参数’5’只取缓冲区中的前4个字符,所以str取的是"1234",而字符’5’仍在缓冲区中,所以cin>>ch直接从缓冲区中取得数据,没有从键盘读取数据!
- 也就是当前一次读取数据出错后,如果缓冲区没有清空的话,重置错误标志还不够!要是能将缓冲区的残留数据清空了就好了哦!下面我们再来看一个很重要的函数!
2.3.9. basic_istream&ignore(streamsize _Count = 1, int_type _Delim = traits_type::eof());
- Causes a number of elements to be skipped from the current readposition
- Parameters:
- _Count, The number of elements to skip from the current read position.
- _Delim, The element that, if encountered before count, causes ignore to returnand allowing all elements after _Delim to be read. (引用msdn)\
- 这个函数用来丢弃输入缓冲区中的字符,第一参数定义一个数,第二个参数定义一个字符变量。下面解释一下函数是怎样执行的:函数不停的从缓冲区中取一个字符,并判断是不是_Delim,如果不是则丢弃并进行计数,当计数达到_Count退出,如果是则丢弃字符退出。例:cin.ignore(5, ‘a’); 函数将不断从缓冲区中取一个字符丢弃,直到丢弃的字符数达到5或者读取的字符为’a’。下面我们看个程序例子:
1 | |
- 例子见参考三
2.3.10. 丢弃一个字符
cin.ignore():删除缓冲区的第一个字符
2.3.11. 清除缓冲区
cin.ignore(1024,'\n');cin.ignore(std::numeric_limits<std::streamsize>::max(), '\n');
2.4. 函数输出
2.4.1. getchar()
- getchar();获得一个字符
- 可以读取到空格\n等等的字符。
2.4.2. putchar()
- putchar();输出一个字符
3. 输出
3.1. 标准输出流 cout
- <<流插入符
std::endl:换行,可以输出一个或者多个,等价于\n
3.1.1. 格式化输出
1 | |
3.2. 使用命名空间std
- using namespace std;来直接使用
- cin,cout是C++标准库内置函数但不是关键字。
3.3. 函数输出
- scanf("%d",&a);
- printf("%d",a);
4. 控制符
| 控制符 | 名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| endl | 换行符 | 换行 |
5. 不同类别的I/O处理
- 基于函数库的I/O
- 基于类库的I/O
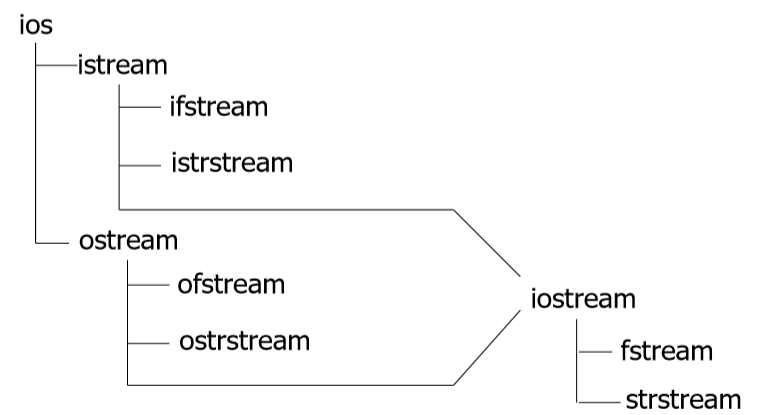
5.1. I/O流库的三类输入/输出
- 控制台I/O:标准I/O设备(cin、cout、cerr、clog)
- 文件I/O
- 字符串I/O
5.2. 重定向
1 | |
5.3. 对操作符<<和>>的重载
- 对自定义类的对象的I/O
- 全局(友元)函数重载
1 | |
5.4. IO处理
1 | |
5.5. Virtualizing constructors 虚拟化构造器
- 虚函数
- 构造器
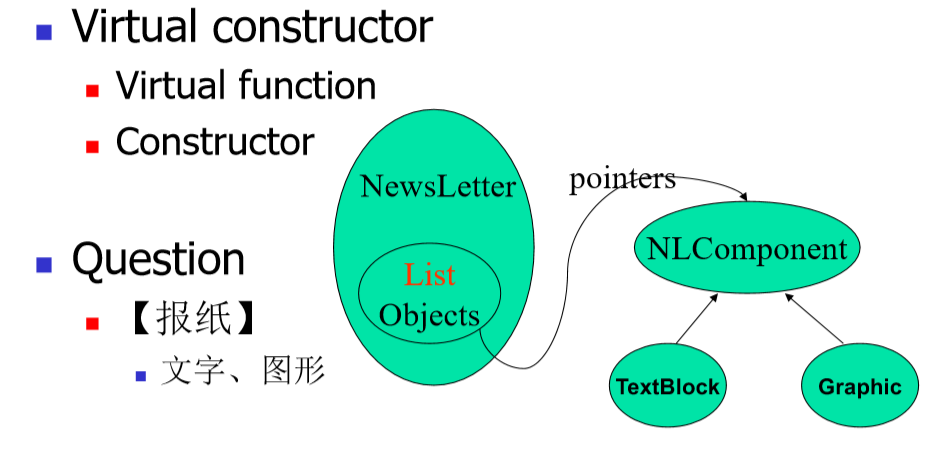
1 | |
6. 读文件
1 | |
7. 泛型用一个方法输出double和int
- 如果
(a - int(a)) > 1E-7:则认为是double - 否则为int
8. 参考
2020-C++高级程序设计-C++ 输入输出
https://spricoder.github.io/2020/07/01/2020-C-plus-plus-advanced-programming/2020-C-plus-plus-advanced-programming-C++%20%E8%BE%93%E5%85%A5%E8%BE%93%E5%87%BA/